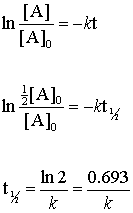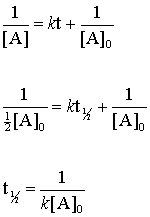half life formula for zero order reaction
The rate constant for a Zero-order reaction rate of constant k. The half-life equation for a zero-order reaction is latext_frac12fracA_02klatex.

Derive The Integrated Half Life Equation For Zero Order Reaction Chemistry Chemical Kinetics 12889537 Meritnation Com
Frac 1 A_02 frac 1 A_0 kt_ 12 frac 1 A_02 - frac 1 A_0 kt_ 12.

. How do you know if its a Zero Order Reaction. The Half-Life of Zero Order Reaction calculator computes the half-life in nuclear decay for a zero order reaction. Substituting these terms into the rearranged integrated rate law and simplifying yields the equation for half-life.
Rate k C12H22O11 Half-Life of a reaction t12. The rate constant k will have units of concentrationtime such as Ms due to. When t t ½ that is the half-life of the reaction completed the concentration of the reactant A A2.
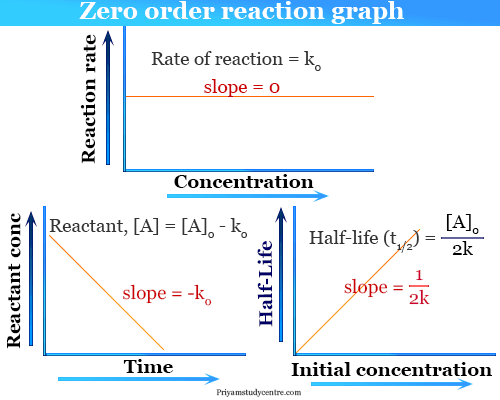
It is to be noted that the half-life of a zero-order reaction is determined by the initial concentration and rate constant. Half life in zero order reaction Half life means 50 percent of reactants disappear in that time interval. A A 0 - kt.
Replace t with half-life t 12. Term half-lifeThe time required for a quantity to fall to half its value as measured at the beginning of the time period. For a zero-order reaction the half-life is given by.
T1 2 A0 2k t 1 2 A 0 2 k A 0 represents the initial concentration and k is the zero-order rate constant. T 12 R 02k From the above relation we can say the Half-Life of a zero-order reaction is directly proportional to the initial concentration of the reactants and inversely proportional to the rate constantt 12 R 02k. T ½ 1 k A o Top.
Determine the half-life of a zero order react. The first-order reaction half-life equation is given by k 2303 t l o g R 0 R From the definition of the half-life of a first-order reaction at t t12 and R R 02. The half-life of a Zero-th order reaction is t A0 2kHere I derive this from the Integrated Rate LawAsk me questions.
The half-life of the reaction is denoted by t 12 and is expressed in seconds. For a zero order reaction A products rate k. For a zero-order reaction the rate law is rate k where k is the rate constant.
For a zero order reaction the formula is t½ Ao 2k. Converting a half life to a rate constant. Remember the half-life of a reaction changes with the order of the reaction.
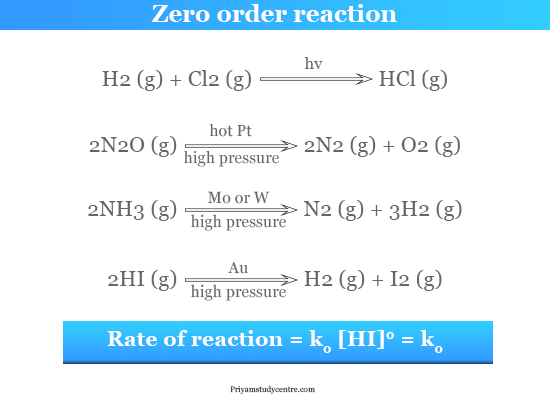
Zero-order reactions are typically found when a material that is required for the reaction to proceed such as a surface or a catalyst is saturated by the reactants. T_frac12 lnfracA_0frac12A_0times frac1k t_frac12 ln2times frac1k. Example of a Zero-Order Reaction The Haber process is a well-known process used to.
T ½ 0693 k For a second order reaction 2A products or A B products when A B rate kA 2. The half-life of a reaction t12 is the time required for one-half of a given amount of reactant to be consumed. What is the half-life of a first-order reaction with a rate constant of 25010-4 s-1Express your.
Determining a half life. If the reactant concentration increases the reaction has zero-order kinetics. Graphical relations and half lives.
Where t12 is the half-life in seconds s and k is the rate constant in inverse seconds s-1. For first order reaction we know that k 1t. Given below is the half-life of a zero-order reaction.
The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is t12 R 02k For the first-order reaction the half-life is defined as t12 0693k And for the second-order reaction the formula for the half. Half-life or t½ is the time that elapses before the concentration of a reactant is reduced to half its initial. The formula for half-life in chemistry depends on the order of the reaction.
In each succeeding half-life half of the remaining concentration of the reactant is consumed. Using the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide see this lesson as an example we find that during the first half. Half-life equation for first-order reactions.
5 rows Zero-Order Reactions. T ½ A o 2k For a first order reaction A products rate kA. T12 A 02K.
Equations for Half Lives. For a zero-order reaction increasing the concentration of the reacting species will not speed up the rate of the reaction. As for other reaction orders an equation for zero-order.
Now we have the following equation and can solve for eqt_ 12 eq. For a first order reaction t½ 0693 k and for a second order reaction t½ 1 k Ao. In the case of a zero-order reaction the rate constant k will be expressed in concentrationtime units such as Ms.
The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t 12 0693k. ½ A A 0 kt 12. Therefore A2 k 0 t ½ or t ½ A2k.
A reaction is zero-order if concentration data is.

Zero Order Reactions Chemistry Class 12 Iit Jee Main Advanced Neet Aipmt Askiitians Youtube

Half Life Expressions Chemistnate
Kinetics Order Of Reactions Ppt Video Online Download
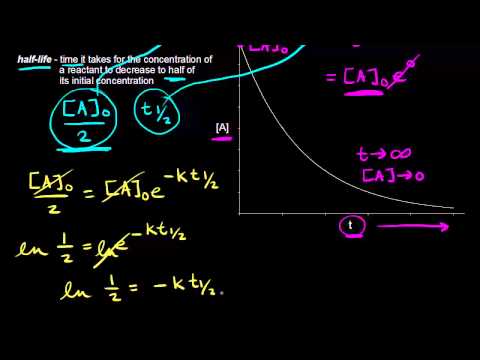
Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Video Khan Academy

Half Life Introduction To Chemistry
Zero Order Reaction Definition Examples Formula

Half Life Of Zero Th 0th Order Reaction Derivation Youtube

Integrated Rate Laws Chemistry For Majors

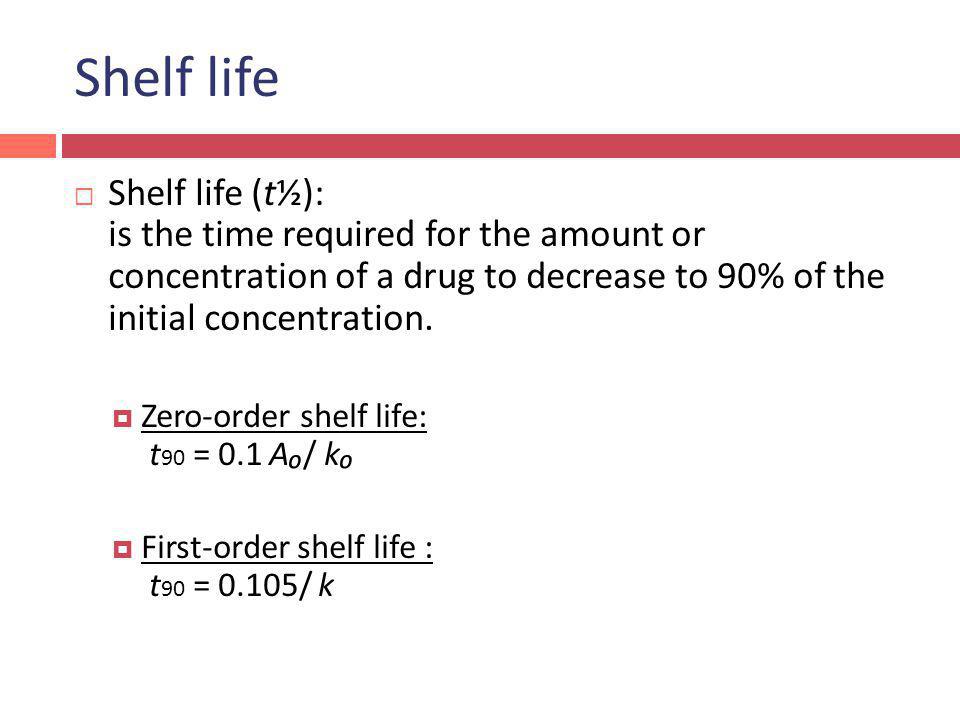
Kinetics And Drug Stability Ed

Which Of The Following Statements Are Corrects

Half Life Expressions Chemistnate
Zero Order Reaction Definition Examples Formula